
Overcome drought 7 days
How mandarin trees overcome 7 days drought better with AMALGEROL, mycorrhiza and soil bacteria
- + increased vigor and vegetative growth
- + 70 % microbiological activity in the soil
- + 60 % mycorrhized roots
Young mandarin nursery trees, planted in pots, are susceptible to abiotic stress when transplanted to the field. Particularly a few days of drought can cause their death. In this trial, we wanted to see if AMALGEROL can harden the nursery trees by increasing their drought tolerance.
The experiment was conducted with 40 young mandarin plants grown in 25-liter pots. Arranged in a randomized complete block design, each treatment (control and AMALGEROL) consisted of 4 replicates with 5 plants each (20 plants per treatment).
AMALGEROL was applied 3 times with 25 ml per pot, approx. once a month, i.e. each plant received 75 ml in total. Right after the last application, the plants were drought stressed for 7 days without any irrigation. After that, the plants were further monitored for a 7-days-recovery phase.
As expected, the AMALGEROL-treated trees showed a better vigor (Fig. 1) and more vegetative growth.
But much more impressive was the following fact (Fig. 2): AMALGEROL-treated plants were able to maintain a significantly higher water potential during the drought stress! How is that possible?
Beside complex metabolic pathways of biostimulants and their stress alleviation, 2 major soil effects were detected:
a) AMALGEROL increased the microbiological activity of the soil by 70 % after its 2nd application (Fig. 3) and
b) AMALGEROL-treated plants had 60 % more mycorrhized roots.
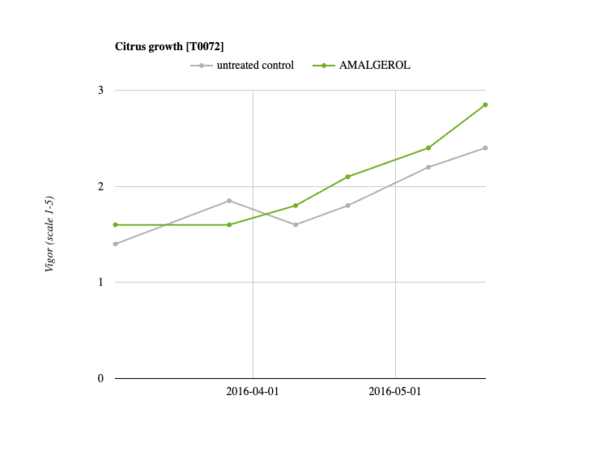 Fig. 1. Plant vigor evolution assessed in a 1-5 hedonic scale. After April 15 th the differences are statistically significant among the treatments (the last 3 measurements).
Fig. 1. Plant vigor evolution assessed in a 1-5 hedonic scale. After April 15 th the differences are statistically significant among the treatments (the last 3 measurements).
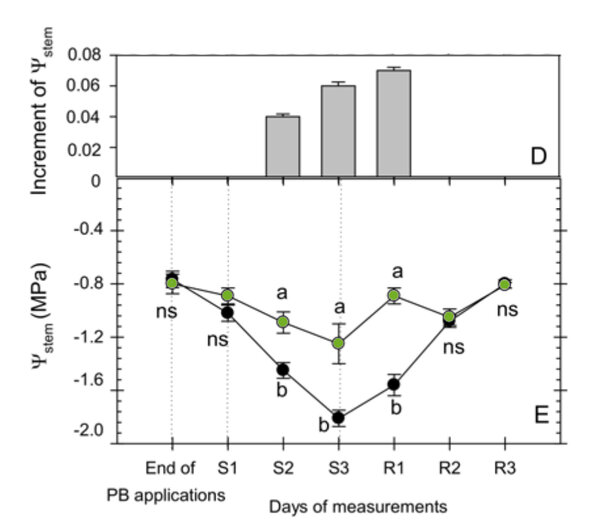
Fig. 2. Seasonal evolution of the midday stem water potential in each treatment (black=untreated, green = AMALGEROL). Values are means with standard errors of 4 replications (n=8 per treatment). Means followed by different letters indicate significant differences between treatments according to LSD0.05 test. ns: not significant. S = Stress phase, R = recovery. S1: 17-May; S2: 19-May; S3; 22-May; R1: 24-May; R2: 26-May; R3: 29-May.
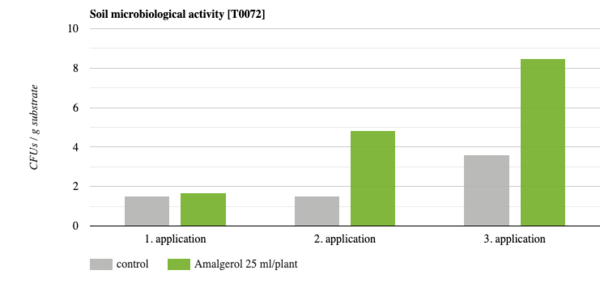
Fig. 3. Microbiological activity quantified as colony forming units (CFUs) of actinomycetes in AMALGEROL and untreated substrates. After the 1. application AMALGEROL samples had 17 % more actinomycetes, after the 2. application 70 % more and after the 3. application 57 % more.
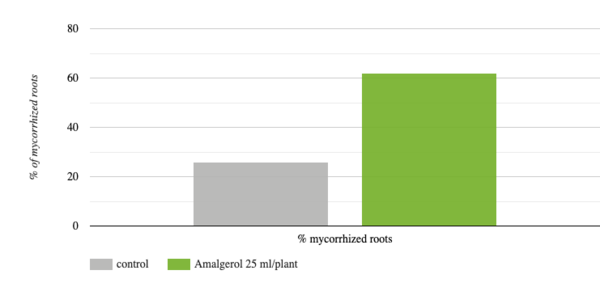
Fig. 4. Mycorrhized roots (%) in untreated and AMALGEROL treated mandarin trees at the end of the experiment (means, n=20). According to the gridline intersect method, roots were prepared and then cut into 100 1-cm fragments per repitition (n = 400 per treatment), and observed under the microscope.
Young mandarin plants

The experiment was conducted with 40 young mandarin plants grown in 25-liter pots.
Details
-
Soil
-
Crop protection:none
-
Treatment
-
Number of treatments: 21. Untreated control2. AMALGEROL, 25 ml/seedling, ABCApplications: 3A. March 11, dissolved in 60 ml water with a syringeB. April 22, as AC. May 15, as A
-
Trial Information
-
Trial location:MurciaTrial country:SpainClimate zone:EPPO MediterraneanCrop:mandarin (Citrus reticulata)
experience Drought stress in tomatoes

Treatment with the biostimulant AMALGEROL ESSENCE has been shown to help significantly reduce or completely prevent damage from drought stress. This is proven by a scientific trial at the Vegenov Institute in France.
experience Speedy lettuce head formation

but also best quality lettuce by boosting head formation with AMALGEROL.
